The Ethiopian military hierarchy has undergone many reorganizations in its structure throughout the periods. This is a military that has witnessed many changes pertaining to structuring, formation and assembling of military ranks. In the early periods, the army was the backbone of the armed forces and constituted about 97 percent of the uniformed services. In the early 1991, the whole army was organized into five revolutionary armies namely:
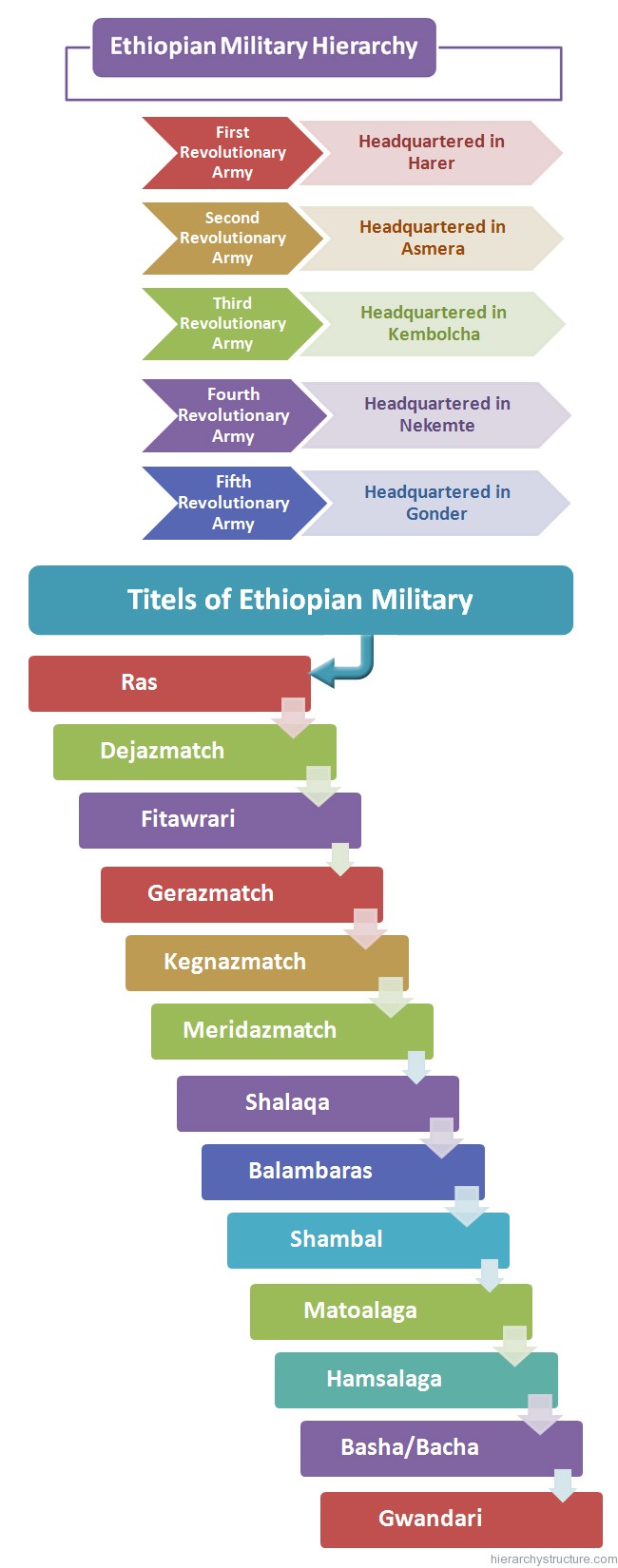
- First revolutionary army, headquartered in Harer.
- Second revolutionary army, headquartered in Asmera.
- Third revolutionary army, headquartered in Kembolcha.
- Fourth revolutionary army, headquartered in Nekemte.
- Fifth revolutionary army, headquartered in Gonder.
The above five revolutionary armies collectively included 31 infantry divisions backed by 32 tank battalions, 40 artillery battalions, 12 air defense battalions and eight commandos brigades. Most of the military equipments used by the Ethiopian army were of Soviet origin.
The titles that are prevalent in the Ethiopian military hierarchy are as follows:
- Ras: This title is equivalent to the General of the modern military system. This rank is the head of the Ethiopian military forces.
- Dejazmatch: This title is equivalent to the Lieutenant General of the modern military organization.
- Fitawrari: This rank is equivalent to the Major General rank of the modern military.
- Gerazmatch: This is analogous to the Brigadier General position of the modern army. It acts as a commander of the left wing of the army.
- Kegnazmatch: This is also analogous to the Brigadier General. It acts as a commander of the right wing of the army.
- Meridazmatch: This is equivalent to the Colonel(staff) rank of the modern military.
- Shalaqa: This is equivalent to the Colonel (line) rank of the modern military. According to the decimal system, this rank is also known as Commander of a thousand.
- Balambaras: This rank is equivalent to the Lieutenant Colonel. This rank acts as the commanders of the guards, cavalry or artillery of an Ethiopia armed force.
- Shambal: This rank is equivalent to the Major. According to the decimal system, this rank is also known as Commander of One hundred fifty.
- Matoalaga: This rank is equivalent to the Captain. According to the decimal system, this is also known as Commander of One hundred.
- Hamsalaga: This rank is equivalent to the Lieutenant.
- Basha/Bacha: This rank is considered as the commander of a rifle corps.
- Gwandari: This is the lowest rank of the Ethiopian military hierarchy, equivalent to the Private of the modern military ranks.
The air force and the naval organizations are also a significant part of Ethiopia military forces. The air force’s strategic organization includes seven fighter ground attack squadrons, one transport squadron and one training squadron. The structure of air force is kept simple, and hence is easier to manage & maintain.
The principal naval bases in Ethiopia were at Mitsiwa and Aseb. Earlier the importance and structuring of naval forces as a separate body was not recognized, but then ,in the year 1958, the navy became an autonomous branch of the armed forces.
Know more about
