The Animal Kingdom is the entire fauna which exists in the nature. The animal kingdom includes all types of animals and there is a specific hierarchy with the help of which they are classified. It is according to their physical traits, habits and habitats. Given below is the Animal Kingdom Hierarchy which helps us to classify the Animals according to different categories so that identifying them becomes easier. This hierarchy is according to the development and evolution of species on earth.
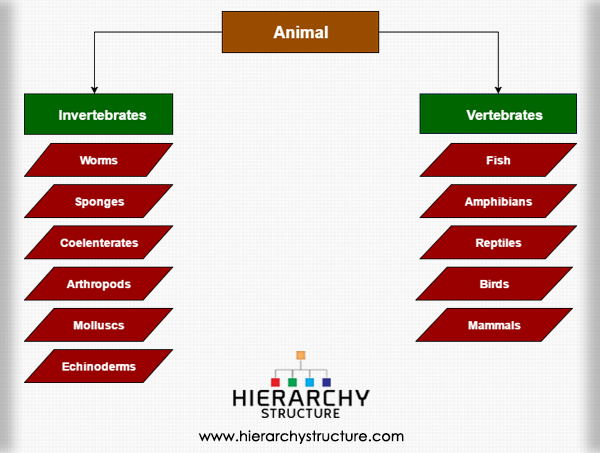
The main categories of animals are:
- Unicellular (Protozoa): The animals which have only one cell are unicellular animals. They are microorganisms whose body is just a single cell. Example: Sarcodina andAmoebozoa.
- Multicellular (Metazoa): The animals whose body is made up of multiple cells are known as multicellular. They include all the other animals except for protozoa.
- Multicellular animals are further classified into:
- Invertebrates: Invertebrates are the animals who do not have bones in their bodies. They are further classified into:
- Worms: Worms are small invertebrates that usually live in the moisture and help in the contribution to degradation of substances.
- Sponges: Sponges are multicellular animals which have pores on their bodies, allowing water to pass directly through it. The examples of sponges include Yellow Tube Sponge, Purple Vase Sponge etc.
- Coelenterates: They are marine species encompassing two animal Phyla. The bodies of these species are hollow and hence, they do not have stability and keep moving with the water flow.
- Arthropods: Arthropods are animals which have an external skeleton covering their body. They have a segmented body and joint appendages. These animals include butterflies, crabs, lobsters etc.
- Molluscs:Molluscs are marine species. They include Octopus, Snails and Squids. They are slimy in texture.
- Echinoderms: Echinoderms are another name for species like Starfish and Sea Cucumber, who have a brittle-like body.
Vertebrates: Vertebrates are the animals who have a backbone and a skeleton to support their body structure. Invertebrate animals include:
- Fish: Fish are marine species who live in water. They have scales and breathe through their gills. They can be carnivorous as well as herbivorous.
- Amphibians: Amphibians are species who can live in the water as well as outside water. They include Frogs, Caecilians and Salamanders.
- Reptiles: Reptiles are cold blooded animals. They include snakes, turtles and lizards. They are cold blooded and hence, their bodies react fast to temperatures and hence, they need to stay in the shade when it is too hot and in warmth when it’s too cold.
- Birds: Birds are endothermic species which are classified with feathers, wings and beak without teeth. They commute by flying in the air but there are a few exceptions to it. Birds include Parrot, Crow, Sparrow, etc.
- Mammals: Mammals are warm blooded animal species who walk on four limbs. They do not lay eggs and procreate directly. Mammals include Tigers, Bears, Lions, Elephants etc. The human is the only mammal who walks on two limbs. Mammals are considered to be the most progressive species of all animals.
Know about Animal Intelligence Hierarchy.
