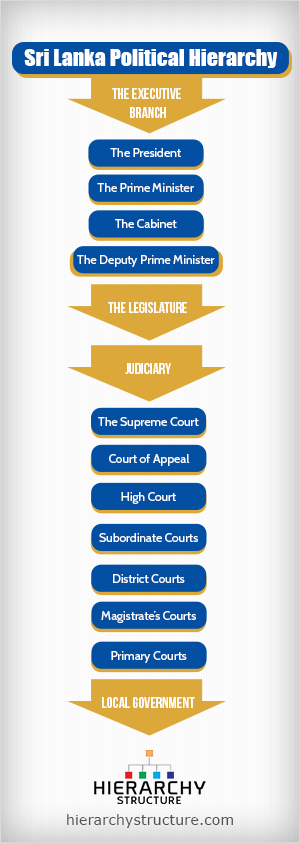
Sri Lanka is a nation which follows a presidential representative democratic republic type of governance in which there is a multi-party rule and the President is both the head of state and head of government. The powers are divided into three legs which are the Executive, the Legislative and the Judiciary.
The judiciary is independent of the legislature and the executive and the country has a diverse and detailed political hierarchy. To know more about the chronologic order of politics in this nation, you can read the following given information.
The Executive Branch
The topmost and the most important branch of the governance system of Sri Lanka is the executive branch. This branch consists of the President who is the highest level official of the nation. The president is the head of the state, head of the government and also the commander in chief of the armed forces. The president is directly elected for a 6 year term. It is the President who appoints and is also the head of the cabinet of ministers who are part of the parliament. The prime minister is the president’s deputy and is the leader of the ruling party of the parliament.
- The President
- The Prime Minister
- The Cabinet-headed by the Prime Minister
- The Deputy Prime Minister
The Legislature
The legislative branch of the government is the parliament which consists of 225 members, each of whom is elected for a 6 year term. The president holds the power to dissolve or suspend the parliament or end a legislative session. It is the legislative branch or the parliament which makes the rules and regulations of the country.
Judiciary
The Judiciary is that branch of the government which is responsible for enforcing law and punishing those who do not follow the laws and rules of the country. The judiciary of Sri Lanka consists of several courts of which the most important is the Supreme Court. The following is the rest of the hierarchy structure of the judiciary of the country.
- The Supreme court
- Court of appeal
- High court
- Subordinate courts
- District courts
- Magistrate’s courts
- Primary courts
Local Government
The local government is divided into two parallel structures-the civil service and the provincial councils. The civil service structure comprises of 25 districts each with a district secretary. On the other hand, the leader of the provincial councils serves as the chief minister along with a board of ministers.