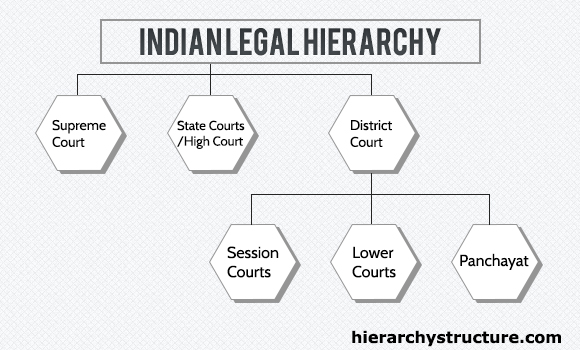
Legal systems are among the most imperative requisites of a country to ensure that it remains a safe & peaceful place to live. The Indian legal system hierarchy or simply saying the Indian Judicial system is partially the British legal system’s continuation, the system which was established in the mid era of the 19th century by English government.
The Indian Judicial system has a systematic arrangement of the all types of courts that exist and run in India currently. Broadly saying this gets divided into 3 levels. The Indian legal system hierarchy is briefly explicated as below in chronological order means starting with the highest level court of the hierarchy and ending with the lowest one:
Supreme Court – In Indian legal system hierarchy, the Supreme Court is at the top level of the Indian court system. The Supreme Court is the utmost authority holder court system in India whose decision can’t be challenged by any other Indian court. If someone wishes to challenge it, he/she has to file a letter to President or Prime Minister of India to do so.
Indian legal system has only one Supreme Court and that is in Delhi, the national capital of India. The Supreme Court came into existence in the year 1950 on 28th of January; soon 2 days after the constitution of India came into continuation. Ever since that time, this highest court has been in Delhi.
State Courts / High Court – The State Courts come direct under the Supreme Court of India in the Indian legal system hierarchy. Every state of India is provided with a court that has the utmost power of judicial system employed in that state only. This state court is termed as High Court and is usually in t
he capital of that particular state. The final decisions for that state’s cases are judged by that court and only Supreme Court has the power & authority to challenge the verdicts that come from High Court decisions.
District Court – Every state of India further incorporates some lower courts that are lower in terms of power and authority than the High Court of that state. These courts are in terms of district means every district of a state has a court that employs maximum government judicial power in that district only. The district court is further subcategorized into 3 parts as below –
- Session Courts – These are a part of District Court with high power. These employ maximum power in a district.
- Lower Courts – These are the lower level courts and most of the times, all the cases of nearby areas are sent to these courts.
- Panchayat – These are a kind of courts basically but in villages where a jury of 5 (or more) people of that village is appointed head and they take care of the local issues. If some issue is beyond their power, those are sent to Lower Court then.