In spite of the fact that, the Army includes a wide collection of weaponry, electronics and communication equipment and fighter vehicles; first and foremost, it is a social organization which is widely known as military unit hierarchy. The most basic and the precious resources of the military are the soldiers. To prevent or rescue the nation from any intruders, both the soldiers and the commanding officers should work in collaboration to undertake all the tasks effectively.
In general, a military force is made up of two components. One is the active component and another is the reserve component. The soldiers represent the active component. They are always on full time active duty. On the other hand, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve represent the reserve components, which are called on duty, as and when needed.
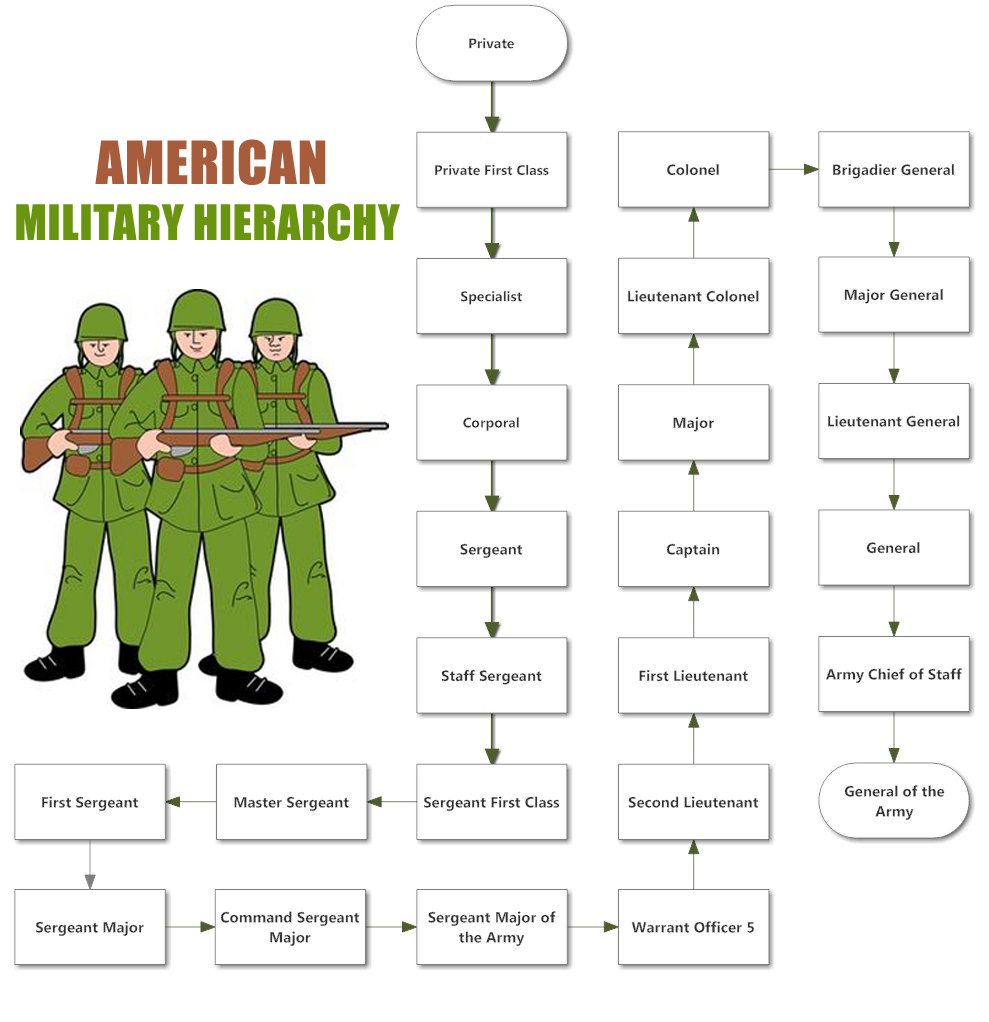
Let’s take a look at the detailed hierarchy of the military units:
- General of the Army: This is the highest position in the army and this position is responsible for supervising all the major and minor army operations.
- Army Chief of Staff: This is the second highest administrative position. The chief acts as principal military advisor and reports to the General.
- General: The generals serve the force in different forms. They act as advisors or commanders, as and when needed. They also serve as central Military command.
- Lieutenant General: The lieutenant generals serve as the leaders of the corps, which consists of two to six divisions.
- Major General: The major general generally commands the divisions, comprised of four to twelve brigades.
- Brigadier General: The Brigadier general also commands the various divisions, like that of the Major general.
- Colonel: The Colonels are commanders of Brigades and they lead four to twelve battalions approximately. They also serve as advisors as per the particular needs of the army.
- Lieutenant Colonel: A lieutenant colonel serves as a commander of the battalions.
- Major: The Major typically comes under the staff position. They commonly serve the army in the form of battalion executive officer or Brigade executive officer. They serve second in command to the battalion commander.
- Captain: A Captain is the highest position, which goes out on the missions with the troops. They lead the companies. The captains also serve as battalion staff officers serving the operations and communication needs of the battalions.
- First Lieutenant: The First Lieutenant leads Platoons.
- Second Lieutenant: The Second Lieutenant also commands the Platoons.
- Warrant Officer 5: The Warrant officers are highly skilled and specialist officers. They serve as technical experts, providing valuable information to the commanders of the organization. They are of various levels such as Warrant Officer 5, 4,3,2,1.
- Sergeant Major of the Army: The Sergeant Major serves as the senior advisor to the general secretary of the Army.
- Command Sergeant Major: The Command Sergeant Major leads the Battalion of three to six Companies.
- Sergeant Major: A Sergeant Major can lead Brigade, Division and corps.
- First Sergeant: The First Sergeant leads a Company of three to six platoons.
- Master Sergeant: The Master Sergeant coordinates and observes the work of the First Sergeant and Sergeant Major.
- Sergeant First Class: The Sergeant First Class leads a Platoon of two to five Squads.
- Staff Sergeant: The Staff Sergeant leads a Squad of two to four teams.
- Sergeant: A Sergeant commands a team of approximately three to ten soldiers.
- Corporal: A corporal is a team leader or second in command of a squad of soldiers.
- Specialist: They are assigned supervisory or clerical duties.
- Private First Class: This rank is held by the junior enlisted candidates.
- Private: Private is a military rank equivalent to a soldier.
