Turkey follows a strictly secular parliamentary representative democratic republic where the Prime minister is the head of the government whereas the president is the head of state. It follows a multi party system. The political system is divided into three branches like that in many other countries-executive, legislative and the judicial branch. This political system is based on the separation of powers and this separation makes governance easy.
The country’s political system functions on the basis of the rules of the constitution and one must comply with it in a very strict manner. To understand the political hierarchy of Turkey better, you can go through the information which has been given as follows.
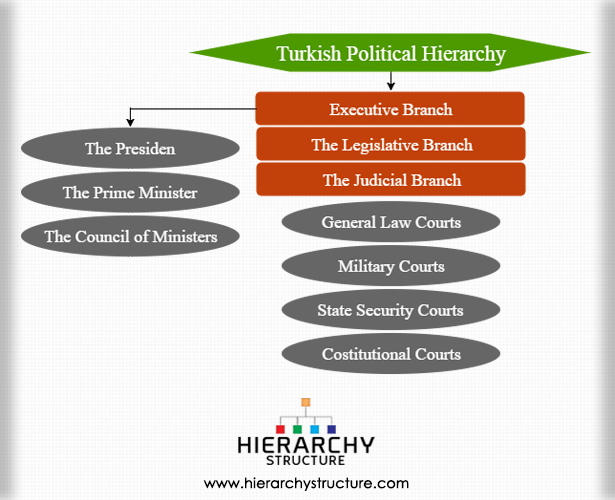
Executive branch
The highest level branch in the Turkish political system is the executive branch. The executive power is mainly exercised by the council of ministers. The head of this branch is the president who is also the head of state and even the prime minister is part of this branch. The prime minister is appointed by the president.
- The president
- The prime minister
- The council of ministers
The legislative branch
The next highest branch in the Turkish political hierarchy is the legislative branch. The legislative power in Turkey is vested in the 550 seat Grand National assembly of Turkey which represent 81 provinces. All the members of this branch are elected for a four year time period out of which one of them serves as the speaker. The current speaker of this branch is Cemil Cicek.
The judicial branch
The judiciary in turkey is independent of the executive and legislative wings and is highly structured. The following is a further division of the judicial branch into 4 main types of courts:
- General Law courts-these courts include criminal civil and administrative courts the high court’s come within this particular level or branch of courts in the country.
- Military courts-these courts have jurisdiction over military personnel and within this category come the courts of first instance and military courts of appeals.
- State security courts-these are composed of a 5 member panel and deal with crime related cases which could be directly related to security of the state.
- Constitutional courts-these are the courts that are meant to review the constitutionality of legislation at the time of passage in context of review of constitutional issues and when requested by the required percentage of the members of the parliament.
This is the structure of Turkish political Hierarchy. Also know about Greek political Hierarchy.